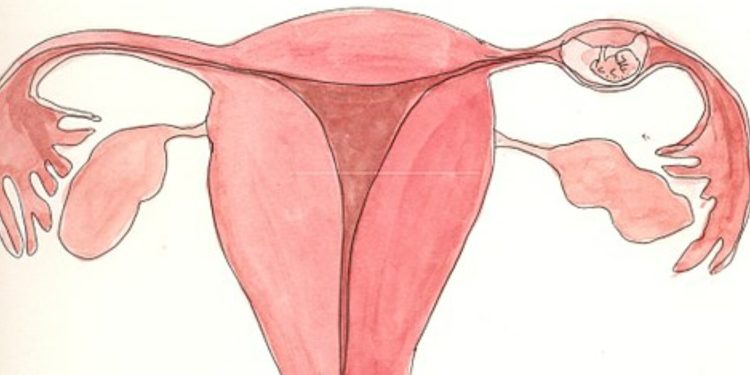
Ectopic pregnancy is a potentially life-threatening condition in which a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes. This condition requires prompt medical attention and intervention, as it can lead to serious complications if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of ectopic pregnancy, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg does not reach the uterus and instead implants in a location outside of it. There are several factors and conditions that can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy:
- Fallopian Tube Damage: The most common cause of ectopic pregnancy is damage or scarring to the fallopian tubes. This can result from previous infections, surgeries, or conditions like endometriosis.
- Inflammation and Infections: Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can cause inflammation and scarring in the reproductive organs, increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Previous Ectopic Pregnancy: Women who have experienced an ectopic pregnancy in the past are at a higher risk of having another one.
- Contraceptive Methods: While birth control methods like IUDs and tubal ligation are highly effective at preventing pregnancy, there is still a small risk of ectopic pregnancy. Consult a best gynecologist in lahore to know more.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Recognizing the symptoms of ectopic pregnancy is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. The signs and symptoms can vary from woman to woman, but common ones include:
- Abdominal Pain: Mild to severe abdominal or pelvic pain is one of the hallmark symptoms of ectopic pregnancy. It is often described as sharp, stabbing pain on one side.
- Vaginal Bleeding: Some women experience vaginal bleeding, which may be lighter or heavier than a normal period.
- Shoulder Pain: In rare cases, the blood from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy can irritate the diaphragm, causing shoulder pain.
- Dizziness and Weakness: As the ectopic pregnancy progresses, it can lead to internal bleeding, causing dizziness, lightheadedness, and weakness.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea can also be associated with ectopic pregnancy due to irritation of the abdominal cavity.
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
Diagnosing ectopic pregnancy is a critical step in preventing complications. Healthcare providers use a combination of medical history, physical exams, and diagnostic tests to confirm the condition:
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: This is often the primary method used to diagnose ectopic pregnancy. It allows healthcare providers to visualize the reproductive organs and identify the location of the gestational sac.
- Blood Tests: A blood test to measure the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced during pregnancy, can provide important information. In an ectopic pregnancy, hCG levels may rise more slowly than in a normal pregnancy.
- Pelvic Exam: A pelvic exam may reveal tenderness or pain in the pelvic area.
Treatment Options for Ectopic Pregnancy
Once ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed, prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications like rupture and severe bleeding. Treatment options include:
- Medications: In cases where the ectopic pregnancy is detected early and has not yet caused significant damage, a medication called methotrexate may be administered. Methotrexate works by stopping the growth of the embryo, allowing the body to reabsorb it.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: If the ectopic pregnancy has progressed or if there is a risk of rupture, laparoscopic surgery may be necessary. This minimally invasive procedure involves removing the ectopic pregnancy and, if needed, repairing any damage to the fallopian tube.
- Laparotomy: In severe cases or when laparoscopic surgery is not feasible, a laparotomy, which is a more extensive abdominal surgery, may be performed to remove the ectopic pregnancy and address any damage.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Ectopic pregnancy can be emotionally challenging for those who experience it. The loss of a pregnancy, coupled with the potential for life-threatening complications, can lead to feelings of grief, guilt, and anxiety. It’s important for individuals and couples to seek emotional support and counseling to cope with these emotions.
Prevention and Future Fertility
While some risk factors for ectopic pregnancy, such as previous fallopian tube damage, cannot be changed, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
- Practice Safe Sex: Reducing the risk of STIs through safe sexual practices can help prevent pelvic inflammatory disease, which is a common cause of fallopian tube damage.
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, quitting can lower your risk of ectopic pregnancy and improve overall reproductive health.
- Early Diagnosis and Treatment: Being aware of the symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention if you suspect an ectopic pregnancy is crucial for a favorable outcome.
- Fertility Concerns: It’s natural to be concerned about future fertility after an ectopic pregnancy. Most women who have had an ectopic pregnancy can still conceive naturally in the future, but close monitoring and consultation with a healthcare provider are advisable.
Conclusion
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition that requires swift diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential for women of reproductive age. Early detection and medical intervention are key to ensuring the best possible outcome and preserving future fertility. Additionally, emotional support and counseling are crucial for those who experience the emotional impact of ectopic pregnancy. By raising awareness and providing education on this topic, we can empower individuals to seek timely medical care and reduce the risks associated with ectopic pregnancy. Visit a gynecologist in Karachi for any concerns you may have.